MSPB State & CAGR
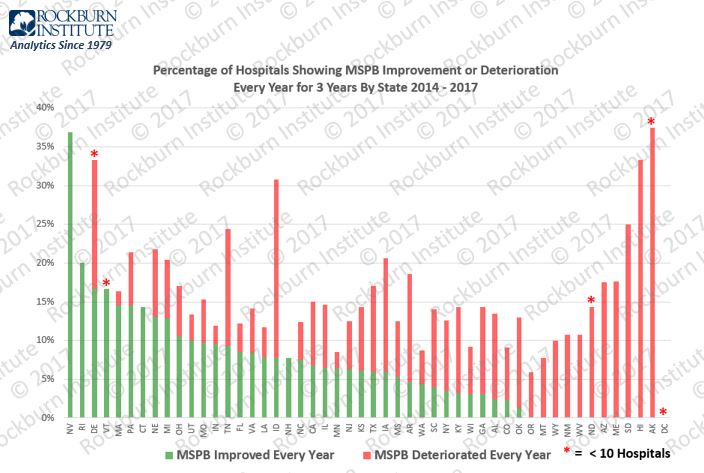
MSPB – Hospital Performance By State – Improving and Deteriorating
Medicare Spending Per Beneficiary (MSPB) measures the efficiency of hospital episodes and is an integral component of Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) quality measurement. We analyzed four years of CMS Hospital Compare datasets for MSPB (CY 2014-17). We grouped 3,070 hospitals by state. The graphic illustrates by state the percentage of hospitals with three-year improvement each year and the percentage of hospitals with a three-year deterioration each year.
Contact us if you wish additional state specific information
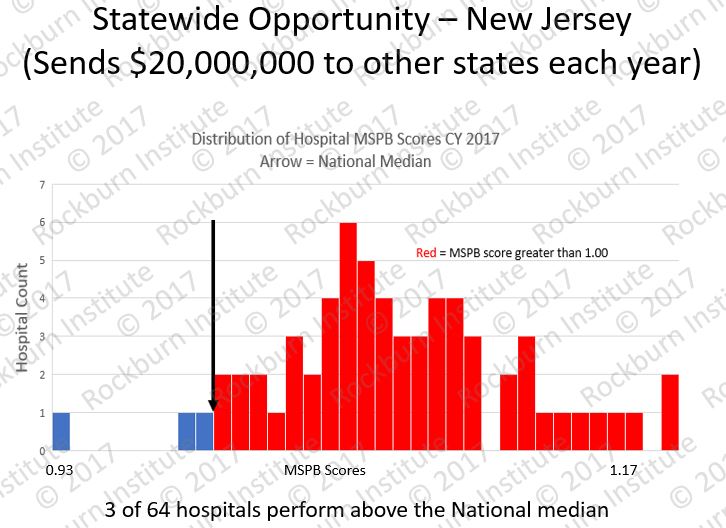
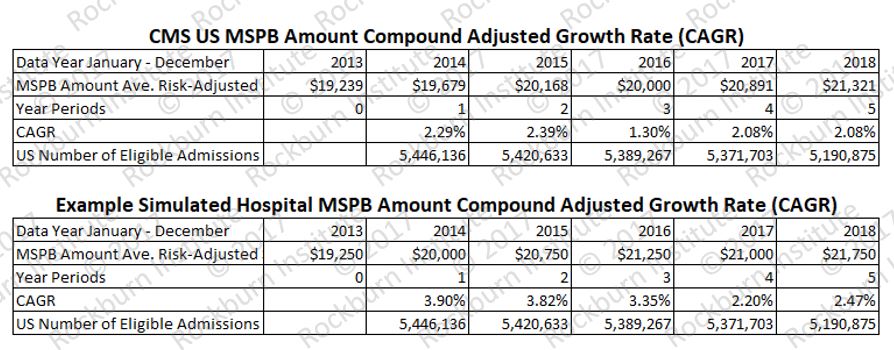
General guidance: MSPB CAGR results reflect MSPB payments for index admissions and 3 days pre and 30 days post-discharge. Unusual cases are excluded. Therefore, MSPB CAGR reflects stable processes of care by eliminating atypical beneficiaries. The exclusions are.
- ‘Transfer’: acute-to-acute transfers.
- ‘Death’: at any time during the index admission or during the MSPB episode, the beneficiary becomes deceased.
- ‘Non-FFS’: IP stays where, at any time from 93 days pre-index admission to 30 days post-discharge from index admission, the beneficiary is not continuously enrolled in Medicare FFS.
- ‘PrmPayer’: IP stays where, at any time from 93 days pre-index admission to 30 days post-discharge from index admission, Medicare is the secondary payer.
- ‘Non-Index Own Episode’: Admissions that occur within 30 days of an index admission and have the same provider are excluded as a new index admission.
- ‘Non-Index Another Provider Episode’: Admissions that occur within 30 days of an index admission and have a different provider are excluded, as a new index admission.
- ‘Outlier_Episode’: MSPB episodes whose residuals fall above the 99th percentile or below the 1st percentile of the distribution of residuals are excluded from the MSPB calculation.
